Attribution modeling helps businesses understand which marketing channels and customer touchpoints drive conversions. By accurately assigning credit to different interactions along the customer journey, companies can optimize marketing spend, improve ROI, and make data-driven decisions about their customer acquisition strategy.
Attribution Models
In this article, we’ll implement a simple yet powerful attribution model using Python and Polars. We’ll focus on two fundamental approaches: first-touch attribution, which assigns conversion credit to the initial customer interaction, and last-touch attribution, which credits the final touchpoint before conversion.
Conceptual Understanding
Let’s start with an example. An ecommerce company wants its users to complete transactions on its website. It runs campaigns targeting customers via SMS, WhatsApp, and email, requesting them to take action on the platform (in this case, making a transaction). All the requests or call-to-action communications sent to the customers are stored in a table. We name this table as call to action table or briefly CTA table. A sample version of the table would be:
| custID | channel | message | timestamp |
|--------|---------|--------------|------------|
| C1 | SMS | Get 5% off | 2025-04-01 |
| C1 | eMail | Get 10% off | 2025-04-05 |
| C1 | WhatsApp| Get 3% off | 2025-04-07 |Next, we have a table which stores all the actions or transactions performed by the customers. We’ll name this table as action table. Such a table would look like:
| custID | txn_ID | amount | timestamp |
|--------|--------|--------|------------|
| C1 | t1 | 250 | 2025-04-06 |
| C1 | t2 | 175 | 2025-04-08 |
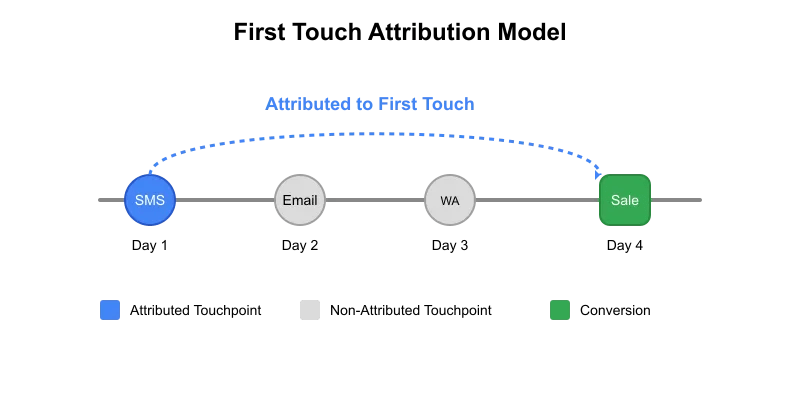
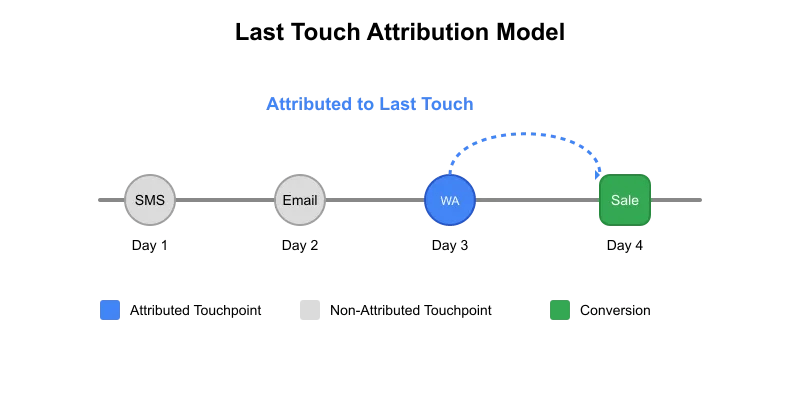
We sent three different calls to action (CTAs) to the customer, and in return, they performed two transactions. We want to see how effective these CTAs were. Based on the first touch attribution, both transactions can be attributed to SMS as that was the first communication sent to the customer. However, if we use the last touch method, transaction t1 will be attributed to email while transaction t2 will be attributed to WhatsApp.

Code based on Polars in Python
Lets start be preparing the tables:
import polars as pl
from datetime import datetime
# Create data for click to action (cta) table
data = [
{"custID": "C1", "channel": "SMS", "message": "Get 5% off", "cta_timestamp": datetime(2025, 4, 1)},
{"custID": "C1", "channel": "eMail", "message": "Get 10% off", "cta_timestamp": datetime(2025, 4, 5)},
{"custID": "C1", "channel": "WhatsApp", "message": "Get 3% off", "cta_timestamp": datetime(2025, 4, 7)}
]
# Create CTA Table
cta_table = pl.DataFrame(data)# Create a Polars DataFrame for the transactions
action_table = pl.DataFrame(
{
"custID": ["C1", "C1","C2"],
"txn_ID": ["t1", "t2","t3"],
"amount": [250, 175, 300],
"action_timestamp": [
datetime(2025, 4, 6),
datetime(2025, 4, 8),
datetime(2025, 4, 4)
]
}
)Step 1: Inner Join
Create an inner join between cta_table and action_table. Any CTA done after the actions are useless, and thus we can filter these out.
action_table_attributed = (
action_table
.join(cta_table, on='custID', how="inner")
.filter(pl.col("action_timestamp") >= pl.col("cta_timestamp"))
)| custID | txn_ID | amount | action_timestamp | channel | message | cta_timestamp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str | str | i64 | datetime[μs] | str | str | datetime[μs] |
| C1 | t1 | 250 | 2025-04-06 00:00:00 | SMS | Get 5% off | 2025-04-01 00:00:00 |
| C1 | t2 | 175 | 2025-04-08 00:00:00 | SMS | Get 5% off | 2025-04-01 00:00:00 |
| C1 | t1 | 250 | 2025-04-06 00:00:00 | Get 10% off | 2025-04-05 00:00:00 | |
| C1 | t2 | 175 | 2025-04-08 00:00:00 | Get 10% off | 2025-04-05 00:00:00 | |
| C1 | t2 | 175 | 2025-04-08 00:00:00 | Get 3% off | 2025-04-07 00:00:00 |
Step 2: Remove duplicate rows
The inner join operation in the first step creates duplicate action rows. We’ll need to remove the duplicate rows and keep only the attributed rows. The rows which will be kept depends on the type of attribution we need to apply.
- First touch attribution: We’ll keep the earliest records based on cta_timestamp and then remove all other duplicate rows.
- Last touch attribution: We’ll keep the latest records based on cta_timestamp and remove remaining.
# First Touch Attribution
result_df = (
action_table_attributed
.sort("cta_timestamp")
.unique(subset=["txn_ID"], keep="first")
.sort("txn_ID") # Optional: sort the results by txn_ID
)
# Last Touch Attribution
result_df = (
action_table_attributed
.sort("cta_timestamp")
.unique(subset=["txn_ID"], keep="last")
.sort("txn_ID") # Optional: sort the results by txn_ID
)| custID | txn_ID | amount | action_timestamp | channel | message | cta_timestamp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str | str | i64 | datetime[μs] | str | str | datetime[μs] |
| C1 | t1 | 250 | 2025-04-06 00:00:00 | SMS | Get 5% off | 2025-04-01 00:00:00 |
| C1 | t2 | 175 | 2025-04-08 00:00:00 | SMS | Get 5% off | 2025-04-01 00:00:00 |
| custID | txn_ID | amount | action_timestamp | channel | message | cta_timestamp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str | str | i64 | datetime[μs] | str | str | datetime[μs] |
| C1 | t1 | 250 | 2025-04-06 00:00:00 | Get 10% off | 2025-04-05 00:00:00 | |
| C1 | t2 | 175 | 2025-04-08 00:00:00 | Get 3% off | 2025-04-07 00:00:00 |
Step 3: Unattributed Actions
Not all actions performed by customers will be attributed to a CTA. Get all unattributed actions:
# Get Unattributed Actions
action_table_unattributed = (
action_table
.join(cta_table, on='custID', how="anti")
)
# Append Attributed and Unattributed Table to a final table
final_table = pl.concat([action_table_attributed,
action_table_unattributed],
how="diagonal")
| custID | txn_ID | amount | action_timestamp | channel | message | cta_timestamp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str | str | i64 | datetime[μs] | str | str | datetime[μs] |
| C1 | t1 | 250 | 2025-04-06 00:00:00 | Get 10% off | 2025-04-05 00:00:00 | |
| C1 | t2 | 175 | 2025-04-08 00:00:00 | Get 3% off | 2025-04-07 00:00:00 | |
| C2 | t3 | 300 | 2025-04-04 00:00:00 | null | null | null |
The final table contains all the actions done by the customers. Along with that, it also has CTA columns. Any transaction not attributed to any CTA will have null values in the CTA columns. This attributed table is helpful as it filters out which CTA communications are best for conversions and which are not.
Business Value of Attribution Modeling
Attribution modeling provides invaluable insights that directly impact business performance. By accurately identifying which marketing channels drive conversions, companies can allocate budgets more efficiently, focusing resources on high-performing touchpoints. This targeted approach typically increases conversion rates by 15–25% while reducing customer acquisition costs. Additionally, attribution reveals the customer journey, helping marketers understand how different channels interact and complement each other. This knowledge enables the creation of more effective, multi-channel campaigns that meet customers at critical decision points. Ultimately, data-driven attribution transforms marketing from an expense into a strategic investment with measurable returns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, implementing attribution models with Python and Polars empowers businesses to move beyond guesswork in marketing decisions. This approach scales seamlessly with growing data volumes while providing the flexibility to adapt attribution rules as business needs evolve. Remember that attribution is not a one-time exercise but an ongoing process that should be continuously refined. As your understanding of customer behavior deepens, you can progress to more sophisticated models like time-decay or position-based attribution. By turning raw interaction data into actionable insights, you’ll not only improve marketing efficiency but also enhance the overall customer experience — creating a sustainable competitive advantage in today’s data-driven marketplace.
